Abstract
This paper considers the problem of temporal video interpolation, where the goal is to synthesize a new video frame given its two neighbors. We propose Cross-Video Neural Representation (CURE) as the first video interpolation method based on neural fields (NF). NF refers to the recent class of methods for neural representation of complex 3D scenes that has seen widespread success and application across computer vision. CURE represents the video as a continuous function parameterized by a coordinate-based neural network, whose inputs are the spatiotemporal coordinates and outputs are the corresponding RGB values. introduces a new architecture that conditions the neural network on the input frames for imposing space-time consistency in the synthesized video. This not only improves the final interpolation quality, but also enables to learn a prior across multiple videos. Experimental evaluations show that achieves the state-of-the-art performance on video interpolation on several benchmark datasets.
Model

Video Interpolation
Input Video
CURE
Try Yourself
Slide and see the difference. (Please open with desktop web browser, like Chrome or Safari)
Static Comparasions with SOTA
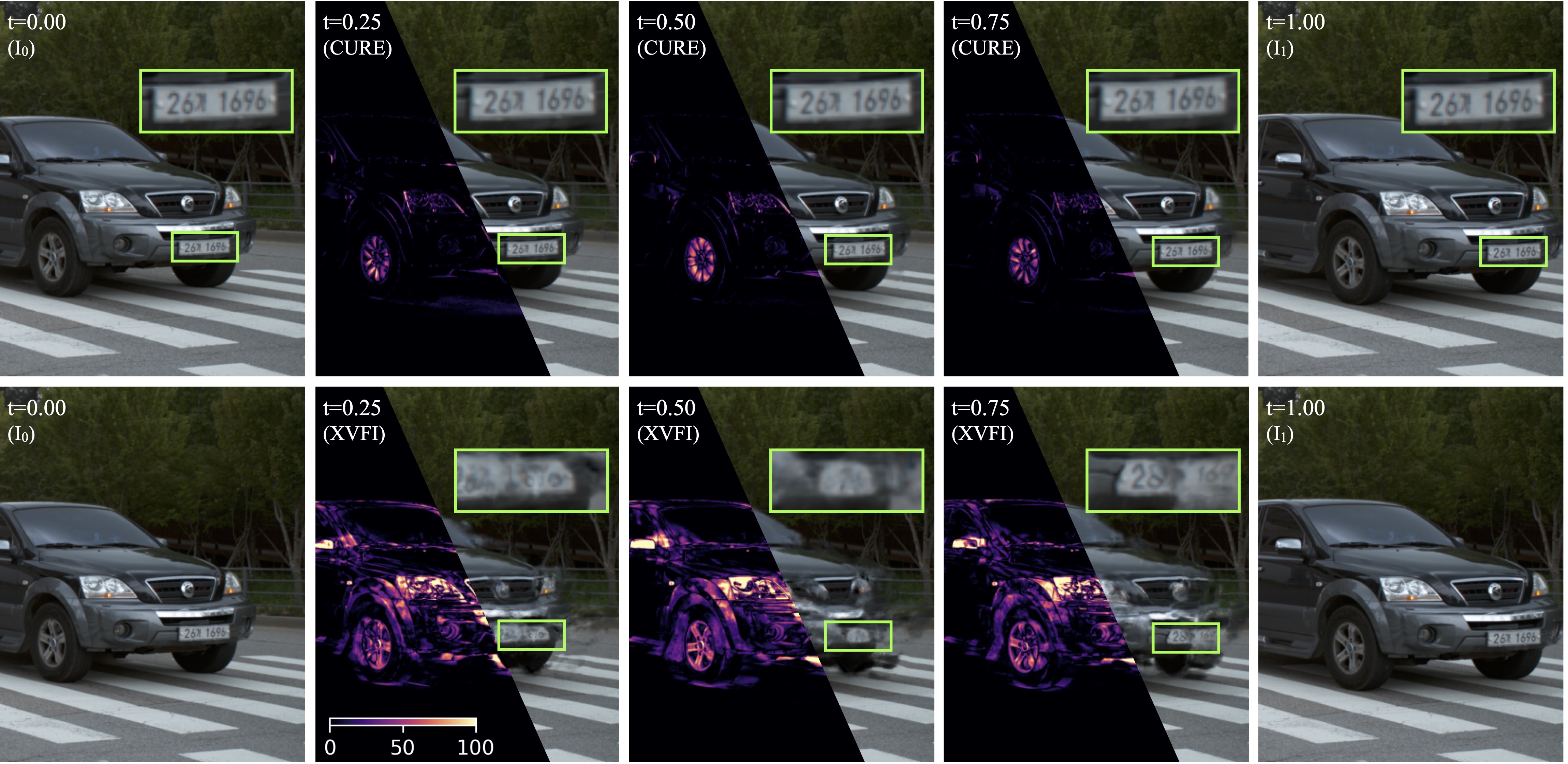
Continuous time interpolation, Car @X4K
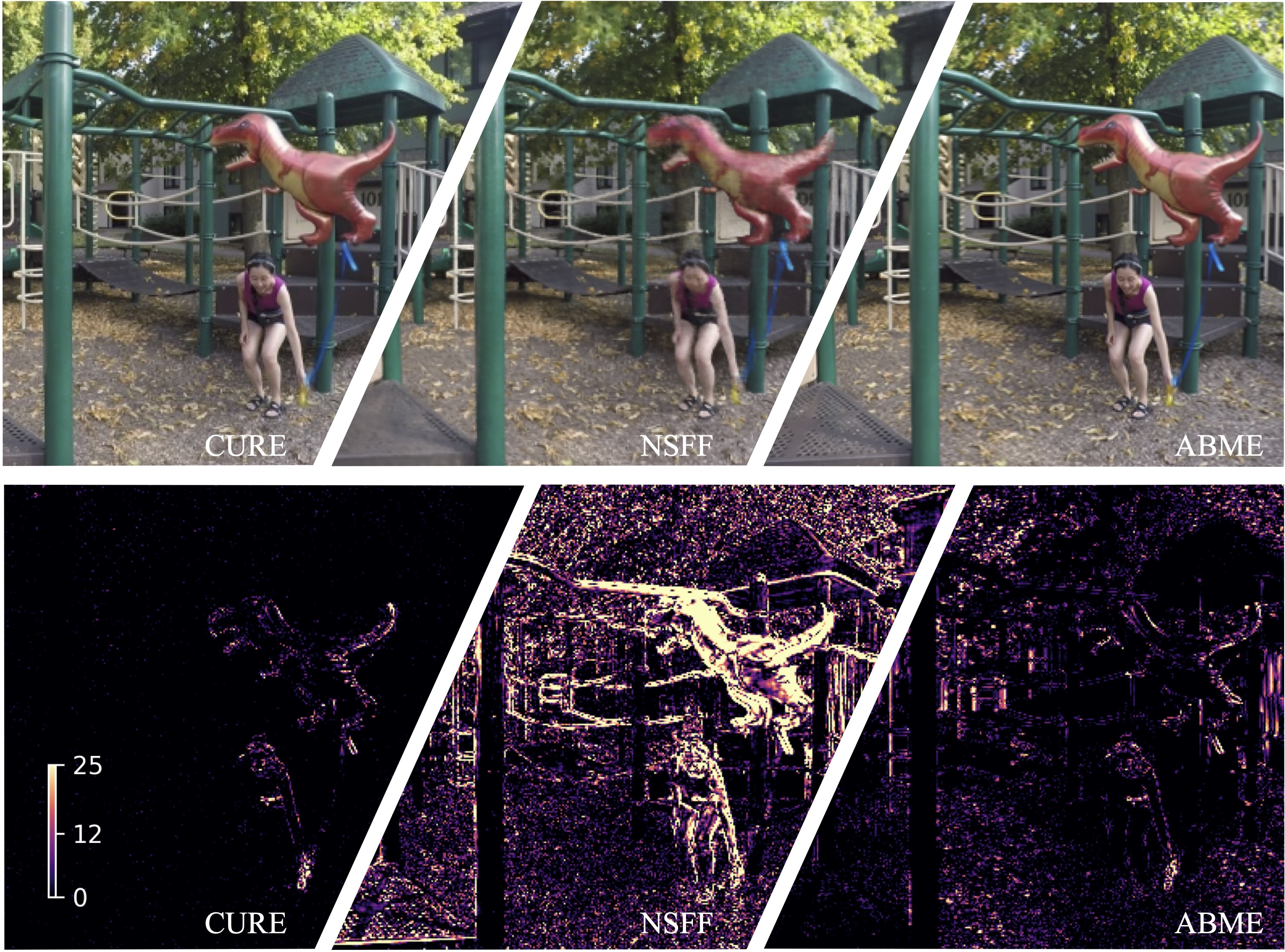

Playground, t=0.5 @Nvidia Dynamic Scene
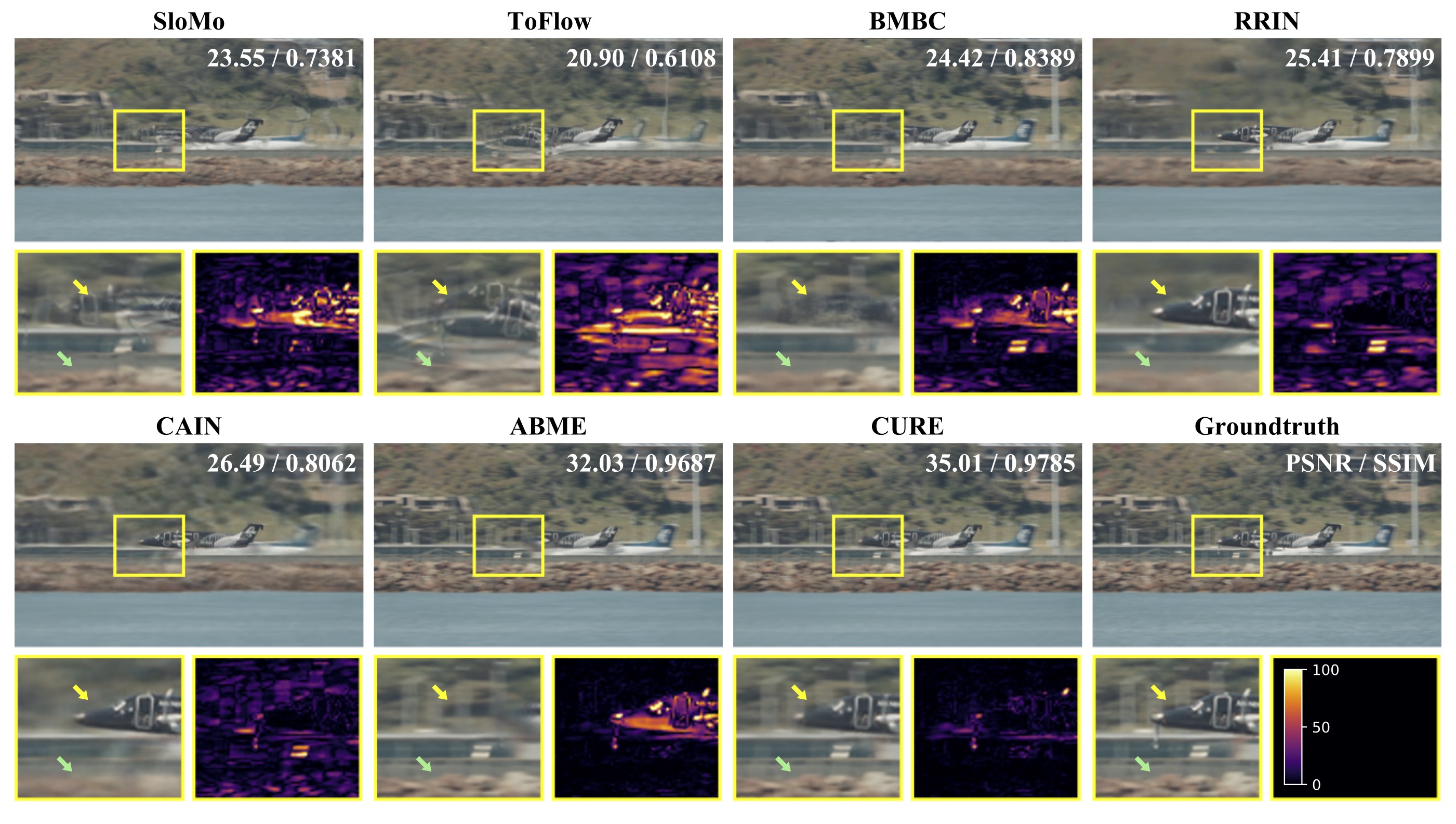
Airplane, t=0.5 @Vimeo90K
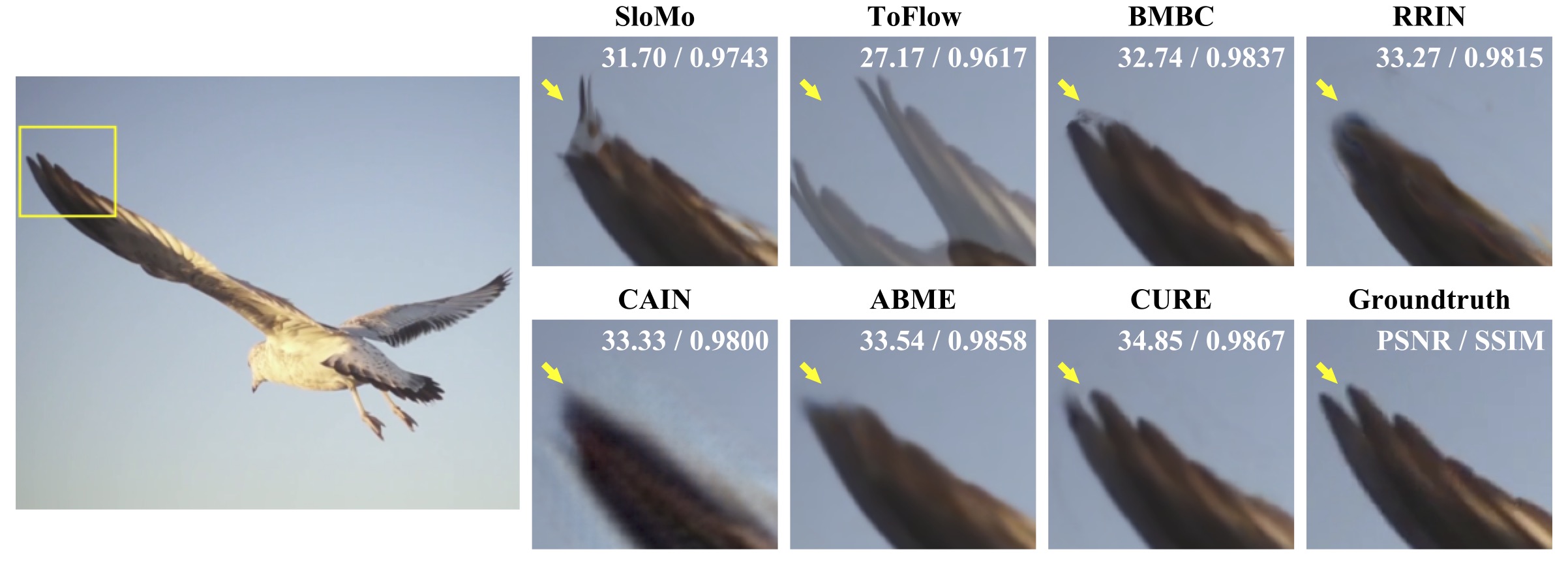

Bird, t=0.5 @SNU-FILM
